Workflows
Managing workflows with the UI
Workflows can be created and managed as entities from the console. You can access them from the dashboard or the left menu. You can:
createa new workflowexpanda workflow to see its 5 latest versionsshowthe details of a workflowedita workflowdeletea workflowfilterworkflows by name and kind
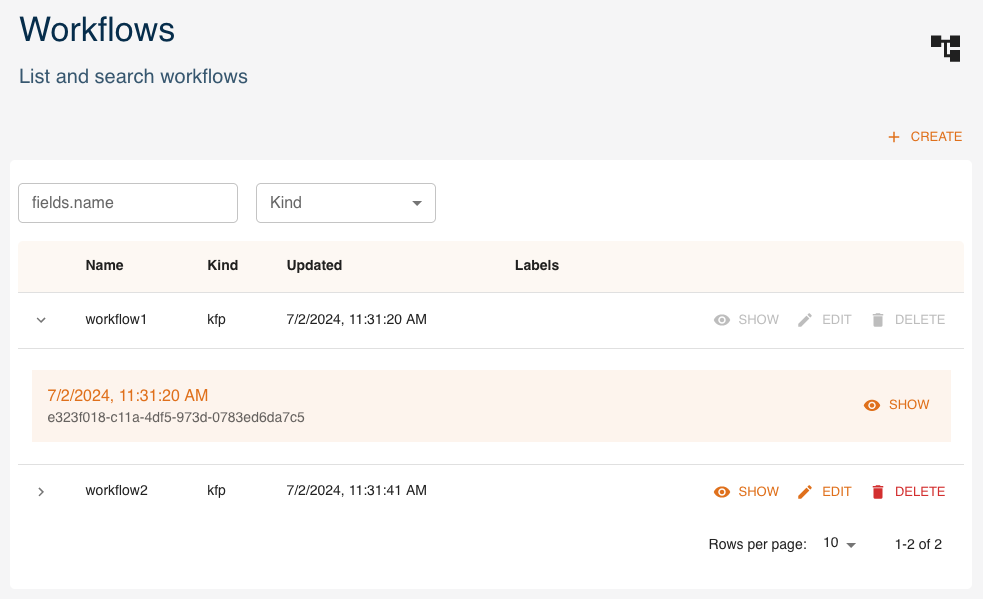
We will now see how to create, read, update and delete workflows using the UI, similarly to what is done with the SDK.
Create
Click CREATE and a form will be shown:
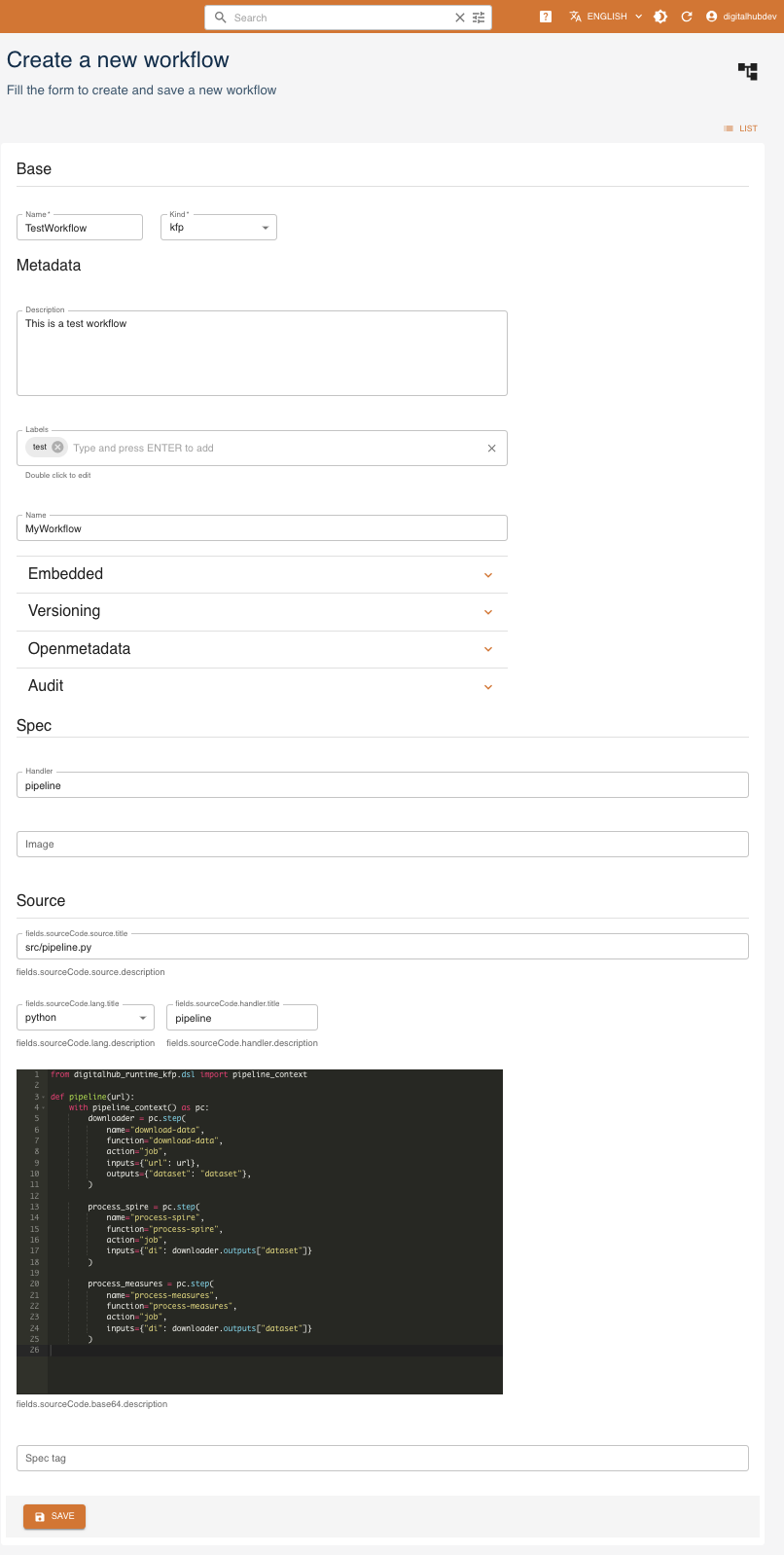
Mandatory fields are:
Name: name and identifier of the workflowKind: kind of workflow
Metadata fields are optional and may be updated later.
Description: a human-readable descriptionLabels: list of labelsName: name of the functionEmbedded: flag for embedded metadataVersioning: version of the functionOpenmetadata: flag to publish metadataAudit: author of creation and modification
In case of a kfp workflow, the fields.sourceCode.source.title field is mandatory as well.
Read
Click SHOW to view a workflow's details.
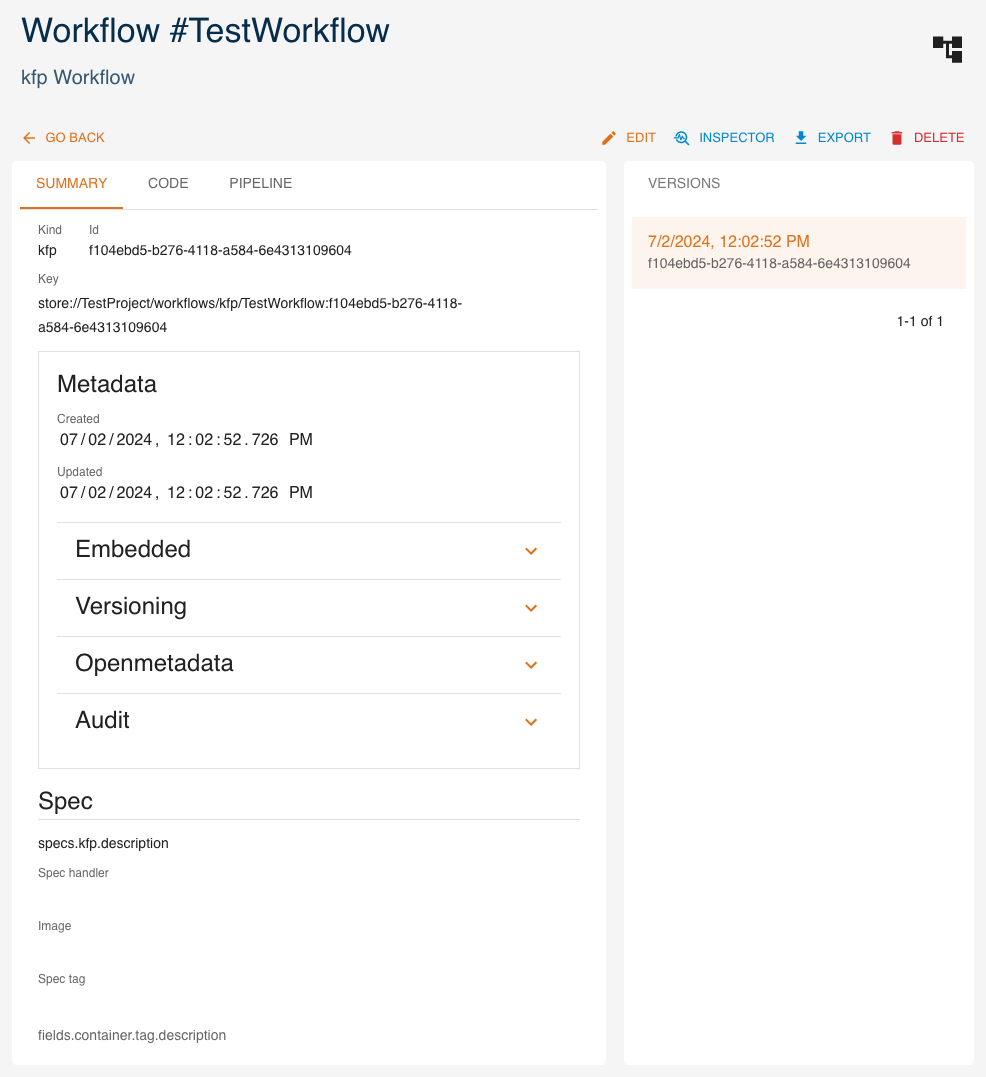
On the right side, all versions of the resource are listed, with the current one highlighted. By clicking a different version, values displayed will change accordingly.
The INSPECTOR button will show a dialog containing the resource in JSON format.
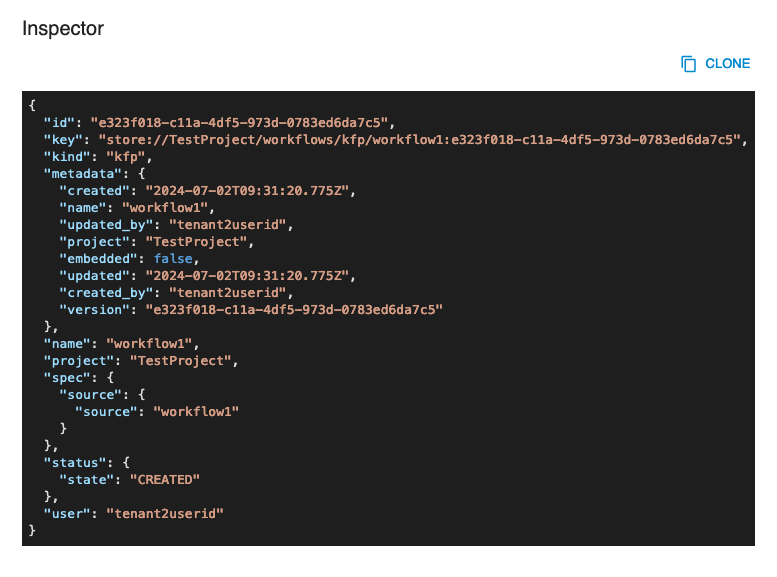
The EXPORT button will download the resource's information as a yaml file.
Update
You can update a workflow by clicking EDIT. Greyed-out fields may not be updated.
Delete
You can delete a workflow from either its detail page or the list of workflows, by clicking DELETE.
Workflow management via SDK
A workflow can be managed with the following methods.
new_workflow: create a new workflowget_workflow: get a workflowupdate_workflow: update a workflowdelete_workflow: delete a workflowlist_workflows: list all workflows
This is done in two ways. The first is through the SDK and the second is through the Workflow object.
Example:
import digitalhub as dh
project = dh.get_or_create_project("my-project")
## From library
workflow = dh.new_workflow(project="my-project",
name="my-workflow",
kind="workflow",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext")
## From project
workflow = project.new_workflow(name="my-workflow",
kind="workflow",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext")
The syntax is the same for all CRUD methods. The following sections describe how to create, read, update and delete a workflow, focusing on managing workflows through the library. If you want to manage workflows from the project, you can use the Project object and avoid having to specify the project parameter.
Create
To create a workflow you can use the new_workflow() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the workflow will be createdname: name of the workflowkind: kind of the workflowpath: remote path where the workflow is stored
Optional parameters are:
uuid: uuid of the workflow (this is automatically generated if not provided). Must be a valid uuid v4.description: description of the workflowsource: remote source of the workflow (git repository)labels: labels of the workflowembedded: whether the workflow is embedded or not. IfTrue, the workflow is embedded (all the spec details are expressed) in the project. IfFalse, the workflow is not embedded in the projectsrc_path: local path of the workflow, used in case of upload into remote storagekwargs: keyword arguments passed to the spec constructor
Example:
workflow = dh.new_workflow(project="my-project",
name="my-workflow",
kind="workflow",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext")
Read
To read a workflow you can use the get_workflow() or import_workflow() methods. The first one searches for the workflow into the backend, the second one loads it from a local yaml.
Get
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the workflow will be created
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the workflow as identifier. It returns the latest version of the workflowentity_id: to use the uuid of the workflow as identifier. It returns the specified version of the workflowkwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
workflow = dh.get_workflow(project="my-project",
entity_name="my-workflow")
workflow = dh.get_workflow(project="my-project",
entity_id="uuid-of-my-workflow")
Import
Mandatory parameters are:
file: file path to the workflow yaml
Example:
workflow = dh.import_workflow(file="./some-path/my-workflow.yaml")
Update
To update a workflow you can use the update_workflow() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
workflow: workflow object to be updated
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
workflow = dh.new_workflow(project="my-project",
name="my-workflow",
kind="workflow",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext")
workflow.metadata.description = "My new description"
workflow = dh.update_workflow(workflow=workflow)
Delete
To delete a workflow you can use the delete_workflow() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the workflow exists
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the workflow as identifierentity_id: to use the uuid of the workflow as identifierdelete_all_versions: ifTrue, all versions of the workflow will be deleted. Mutually exclusive with theentity_idparameter.kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
workflow = dh.new_workflow(project="my-project",
name="my-workflow",
kind="workflow",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext")
dh.delete_workflow(project="my-project",
entity_id=workflow.id)
List
To list all workflows you can use the list_workflows() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project containing the workflows
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
workflows = dh.list_workflows(project="my-project")
Workflow object
The Workflow object is built using the new_workflow() method. There are several variations of the Workflow object based on the kind of the workflow. The SDK supports the following kinds:
kfp: represents a generic workflow
For each different kind, the Workflow object has a different set of methods and different spec, status and metadata.
All the Workflow kinds have a save() and an export() method to save and export the entity workflow into backend or locally as yaml.
To create a specific workflow, you must use the desired kind in the new_workflow() method.
kfp
The kfp kind indicates that the workflow is a generic workflow.
There are no specific spec parameters.
The kfp kind has the following methods:
as_file(): collects the workflow into a local temporary filedownload(): downloads the workflow into a specified pathupload(): uploads the workflow to a specified path
As file
The as_file() method returns the workflow as a temporary file. The file is not automatically deleted when the program ends.
The method returns the path of the downloaded workflow.
Download
The download() method downloads the workflow into a specified path.
The method returns the path of the downloaded workflow.
The method accepts the following parameters:
target: remote path of the workflow to be downloaded (eg.s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext). By default, uses thespecpath.dst: local path where the workflow will be downloaded. By default, it is in the current working directoryoverwrite: ifTrue, the target path will be overwritten if it already exists
Upload
The upload() method uploads the workflow to a specified path.
The method returns the path of the uploaded workflow.
The method accepts the following parameters:
source: local path of the workflow to be uploadedtarget: remote path of the workflow to be uploaded (eg.s3://my-bucket/my-workflow.ext). By default, uses thespecpath.