Projects
A Digital Hub project represents a data and AI application and is a container for different entities (code, assets, configuration, ...) that form the application. It is the context in which you can run functions and manage models, data, and artifacts. Projects may be created and managed from the UI, but also by using DH Core's API, for example via Python SDK.
Managing Projects via UI
In the following sections we document project management via the Digital Hub Console UI.
Here we detail how to create, read, update and delete projects using the UI, similarly to SDK usage.
Create
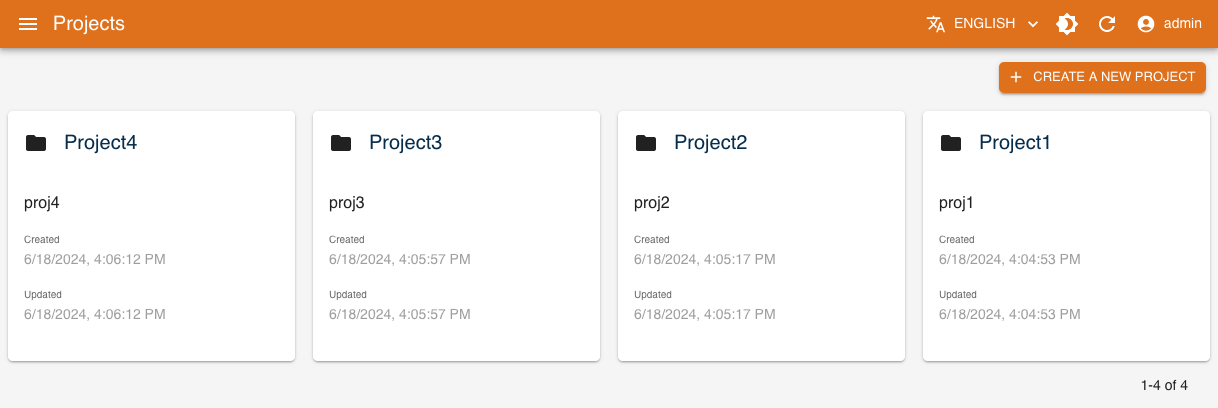
A project is created by clicking CREATE A NEW PROJECT in the console's home page.
A form asking for the project's details is then shown:
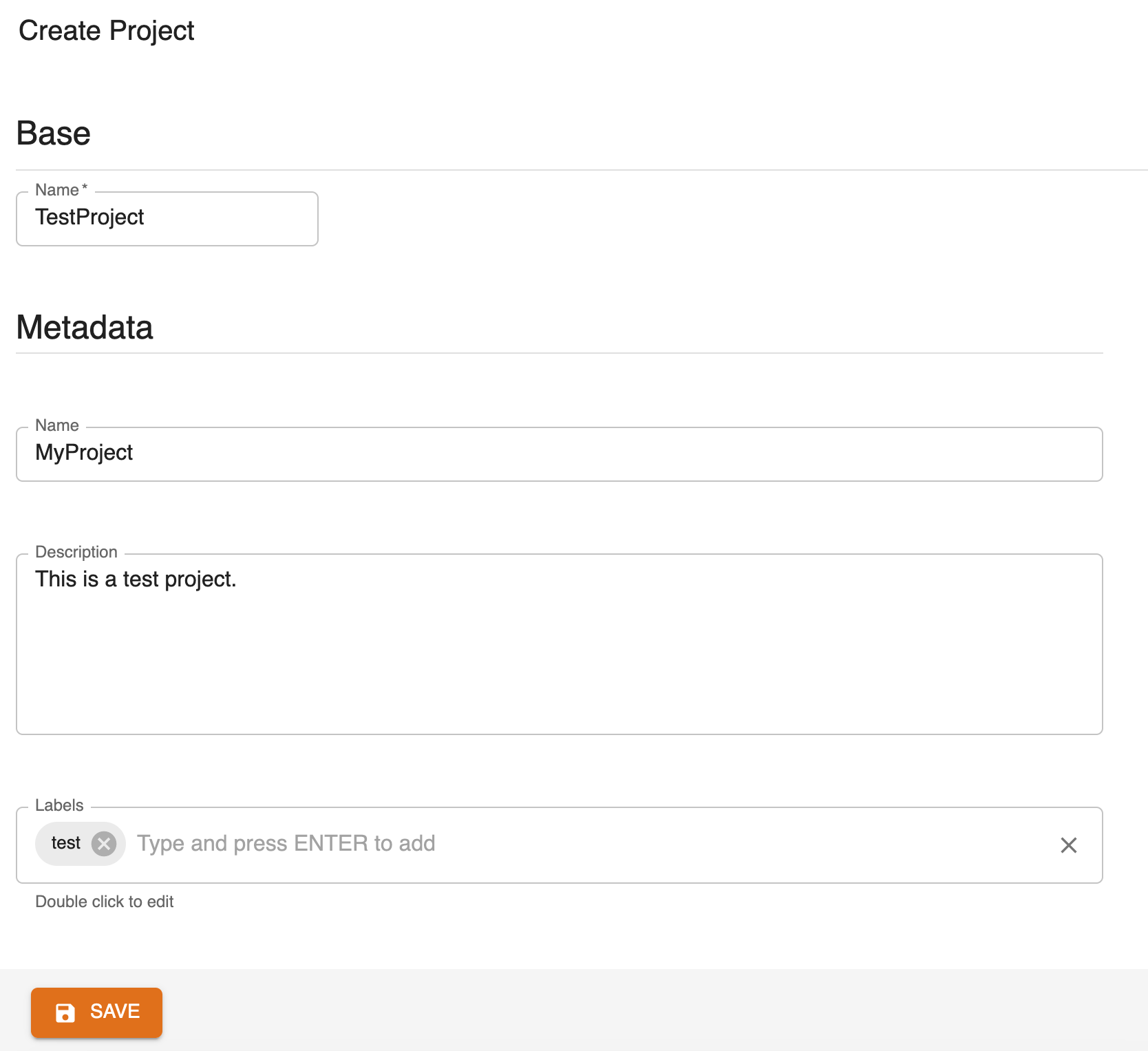
The following parameters are mandatory:
name: name of the project, also acts as identifier of the project
Metadata parameters are optional and may be changed later:
name: name of the projectdescription: a human-readable description of the projectlabels: list of labels
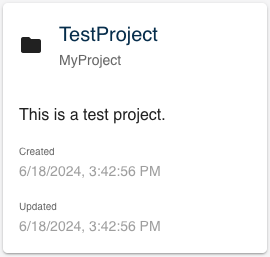
Save and the project will appear in the home page.
Read
All projects present in the database are listed in the home page. Each tile shows:
- Identifier of the project
- Name of the project (hidden if same as identifier)
- Description
- Date of creation
- Date of last modification
Click on the tile to access the project's dashboard:
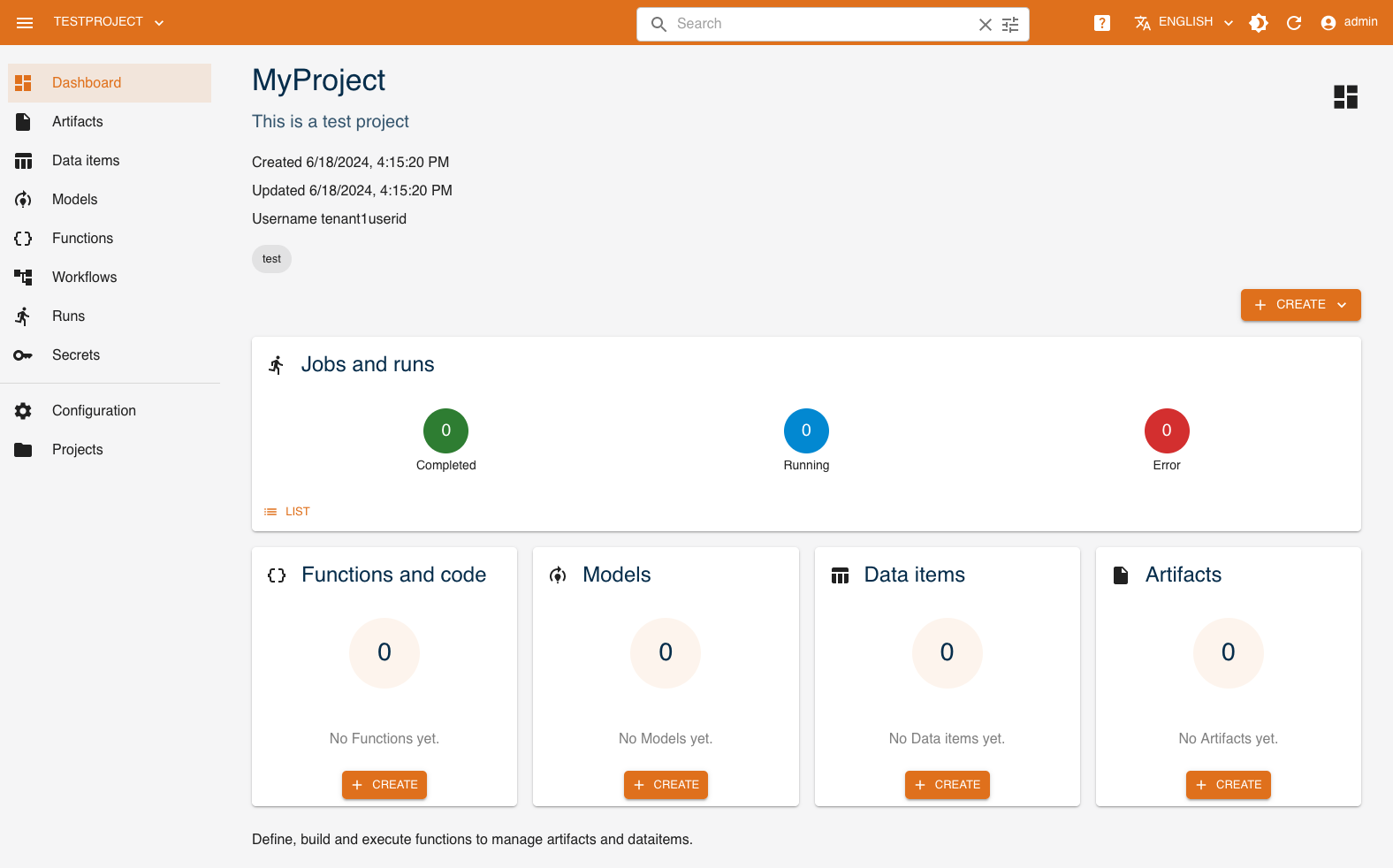
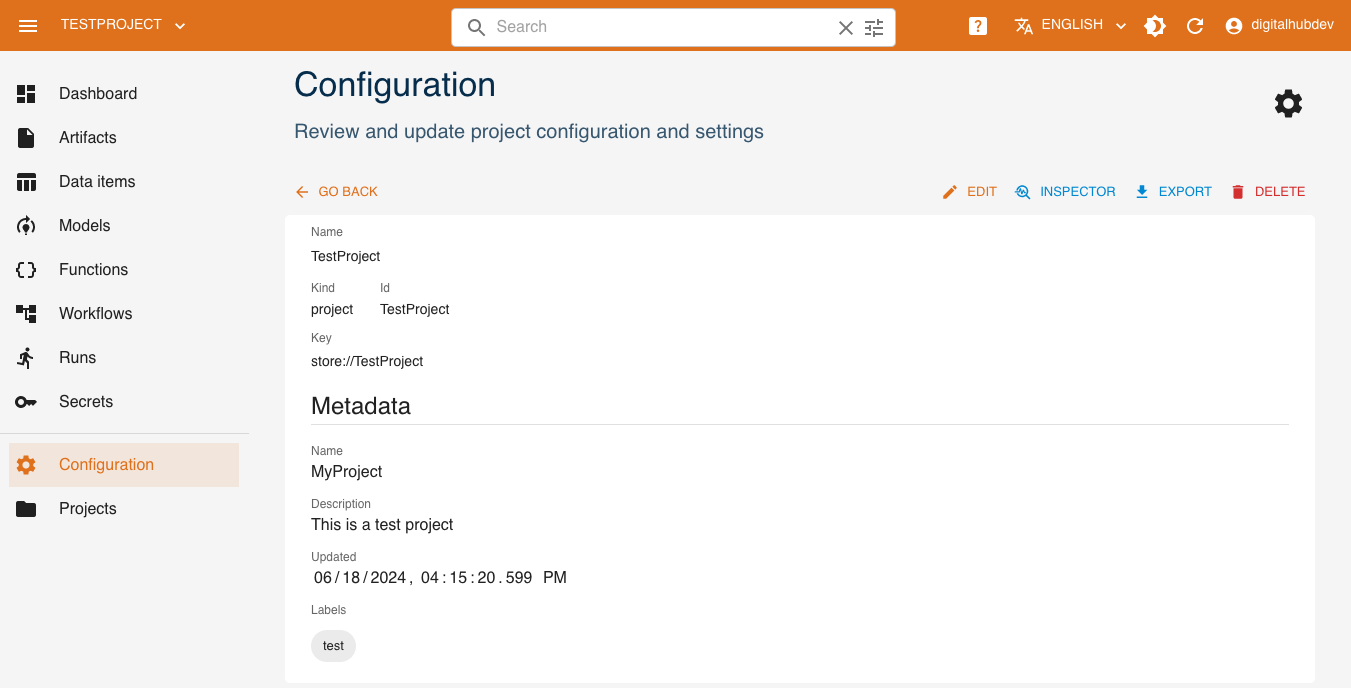
This dashboard shows a summary of the resources associated with the project and allows you to access the management of these resources.
Jobs and runs: list and status of performed runsModels: number and list of latest modelsFunctions and code: number and list of latest functionsData items: number and list of latest data itemsArtifacts: number and list of latest artifacts
You can return to the list of projects at any time by clicking Projects at the bottom of the left menu, or switch directly to a specific project by using the drop-down menu in the upper left of the interface.
Update
To update a project's Metadata, first click Configuration in the left menu.
Click Edit in the top right and the edit form for Metadata properties will be shown. In the example below, a label was added.
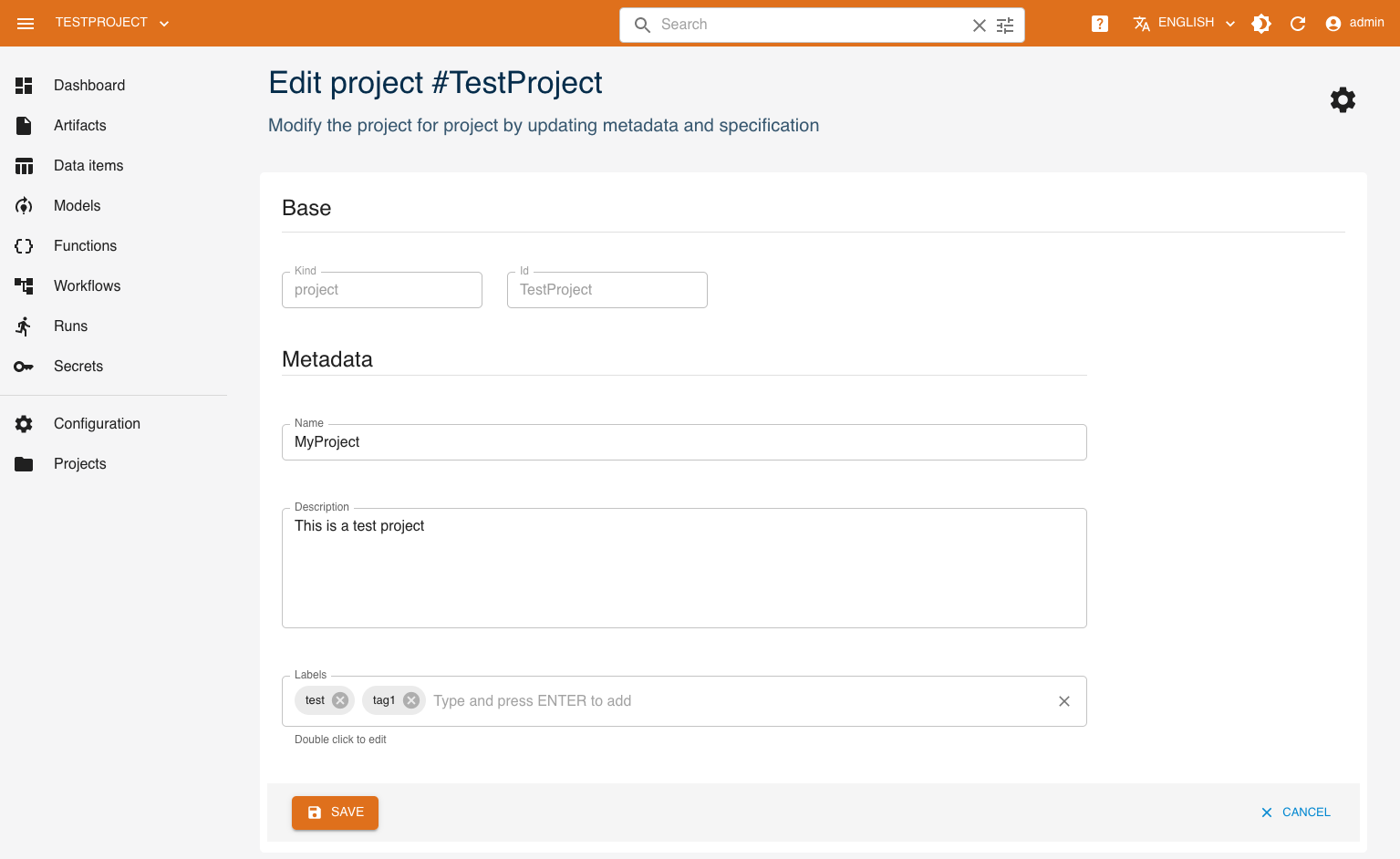
When you're done updating the project, click Save.
Delete
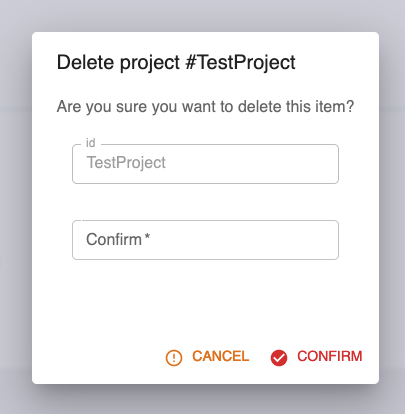
You can delete a project from the Configuration page, by clicking Delete. You will be asked to confirm by entering the project's identifier.
Managing Projects via SDK
In the following sections we document the project CRUD methods available in the SDK and the methods exposed by the Project entity.
Basic Operations
Here we analyze how to create, read, update and delete projects using the SDK.
Create
A project is created with new_project() method. It has the following mandatory parameters:
name: the name of the project, it is also the identifier of the project
The other parameters are optional:
context: path where project can export yaml files locallydescription: a human readable description of the projectsource: a Git repository URL where lies the project codelabels: list of labelslocal: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalseconfig: a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer tokensetup_kwargs: a dictionary containing the project hook setup argumentskwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
import digitalhub as dh
project = dh.new_project("my-project", context="./", description="my new project")
Config
The config parameter can be used to provide a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer token. The format of the dictionary for basic auth must be as this:
{
"user": "user",
"password": "password"
}
The format of the dictionary for bearer token must be as this:
{
"access_token": "token"
}
In case you try to get a project without from the backend with invalid credentials, an exception will be raised.
Because the backend client is a Singleton object, it will autoconfigure credentials at startup, so the only way to setup proper credentials once it fails to connect is to use the SDK method set_dhub_env().
The method accepts the following optional parameters:
endpoint: the endpoint of the backenduser: the user for basic authpassword: the password for basic authtoken: the auth token
Example:
dh.set_dhub_env(
endpoint="https://some-digitalhub:8080",
token="token"
)
Note that the set_dhub_env() method ovverrides the environment variables and (if already instantiated) the credentials attributes of the backend client.
Setup kwargs
The setup_kwargs parameter can be used to provide a dictionary containing the project hook setup arguments. The concept behind this parameter is that at the beginning of the project lifecycle, the project can be configured with an hook script that will be executed when the project is created / got.
First of all, the configuration script MUST comply with the following format:
- It must be a Python script named
setup_project.pyinside the project context directory. - It must contain an handler (a python function) named
setupas entrypoint. - The
setupfunction must accept aProjectinstance as the only positional argument. setup_kwargsmust be passed as keyword arguments to thesetupfunction.
The project setup will create a .CHECK file at the end of the setup function execution. This sentinel file is used to indicate that the project is set up and new executions will be ready.
A use case scenario can be the instantiation of entities used by the user like artifacts or functions.
Example:
setup_kwargs = {
"some_arg1": "arg1",
"some_arg2": "arg2"
}
# Setup script
def setup(project, some_arg1=None, some_arg2=None):
# Do something with project and args
Read
You can read a project with three methods, from remote backend with get_project(), from local directory with import_project() or from either with load_project().
Get project
With get_project() you can load a project from the backend. The method requires the following manadatory parameters:
name: the name of the project
The other parameters are optional:
local: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalseconfig: a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer tokensetup_kwargs: a dictionary containing the project hook setup argumentskwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.get_project("my-project")
Import project
With import_project() you can load a project from a local directory. The method requires the following manadatory parameters:
file: path to the yaml project file
The other parameters are optional:
local: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalseconfig: a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer tokensetup_kwargs: a dictionary containing the project hook setup argumentskwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.import_project("./my-project.yaml")
Load project
With load_project() you can load a project from the backend or from a local directory.
The method requires either one of the following parameters:
name: the name of the projectfile: path to the yaml project file
If you pass the name, the method will try to load the project from the backend, otherwise it will try to load it from the local directory. Note that both parameters are mutually exclusive and keyword arguments.
The other parameters are optional:
local: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalseconfig: a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer tokensetup_kwargs: a dictionary containing the project hook setup argumentskwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.load_project(name="my-project")
project = dh.load_project(file="./my-project.yaml")
Create or read
The digitalhub SDK provides a method get_or_create_project() that allows you to create a project if it does not exist. The method has the following mandatory parameters:
name: the name of the project.
The other parameters are optional:
context: path where project can export yaml files locallylocal: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalseconfig: a dictionary containing the project configuration like user and password for basic auth or a bearer tokensetup_kwargs: a dictionary containing the project hook setup argumentskwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.get_or_create_project("my-project", context="./")
Update
You can update a project with update_project() method. It has the following mandatory parameters:
project: the project entity that will be updated
The other parameters are optional:
kwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.update_project(project)
Delete
You can delete a project with delete_project() method. It has the following mandatory parameters:
name: the name of the project
The other parameters are optional:
cascade: a boolean value, ifTruethe project and all the related resources will be deleted from the backend. Defaults toTrue. It is only available in the Core backend.clean_context: a boolean value, ifTruethe project context will be deleted (no more object can be created locally under the project).local: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be managed without Core backend. Defaults toFalsekwargs: a list of keyword arguments passed to the client that comunicate with the backend
Example:
project = dh.delete_project("my-project")
Project methods
The Project class exposes two basic methods that allow you to save remotely or export locally the project.
Furthermore, according to the SDK digitalhub layer installed, the Project class exposes CRUD methods for a variety of entities.
Save and export
The methods save() and export() are used to save the project on the backend or export the project locally.
Save
The save() method is used to save the project on the backend and it accepts the following optional parameters:
update: a boolean value, ifTruethe project will be updated on the backend
Please note that the save method will usually raise an exception if called without the update parameter on runtime. This is because the project (managed with CRUD SDK methods) should already exists on the backend if exists as object.
Export
The export() method is used to export the project locally as yaml file and it accepts the following optional parameters:
filename: the name of the file to export
Note that the filename must have the .yaml extension. The project will be exported as a yaml file inside the context directory. If no filename is passed, the project will be exported as a yaml file named project_{project-name}.yaml.
According to the SDK digitalhub layer installed, the Project class exposes CRUD methods for a variety of entities.
Entity Management Operations
The project acts as context for other entities as mentioned in the introduction. With a Project object, you can create, read, update and delete these entities. The methods exposed are basically five for all entities, and are:
new: create a new entityget: get an entity from backendupdate: update an entitydelete: delete an entitylist: list entities related to the project
Each digitalhub layer exposes CRUD handles different aspects of data and ml entities. Here follows a list of the methods exposed by the Project class for each layer. Please refer to the specific entity documentation for more information.
Core layer
The entity handled by the Project class in the core layer (digitalhub_core) are:
functionsartifactsworkflowssecrets
Data layer
The entity handled by the Project class in the data layer (digitalhub_data) are:
dataitems
Ml layer
The entity handled by the Project class in the ml layer (digitalhub_ml) are:
models