Data and transformations
The platform supports data of different types to be stored and operated by the underlying storage subsystems.
Digital Hub natively supports two types of storages:
- persistence object storage (datalake S3 Minio), which manages immutable data in the form of files.
- operational relational data storage (PostgreSQL database), which is used for efficient querying of mutable data. Postgres is rich with extensions, most notably for geo-spatial and time-series data.
The data is represented in the platform as entities of different types, depending on its usage and format. More specifically, we distinguish:
- data items, which represent immutable data sets resulting from different transformation operations and are ready for use in differerent types of analysis. Data items are enriched with metadata (versions, lineage, stats, profiling, schema, ...) and unique keys and managed and persisted to the datalake directly by the platform in the form of Parquet files. It is possible to treat tabular data (items of
tablekind) as, for example, DataFrames, using conventional libraries. - artifacts, which represent arbitrary files, not limited to tabular format, stored to the datalake with some extra metadata.
Each data entity may be accessed and manipulated by the platform via UI or using the API, for example with SDK.
Manipulating data via UI
Artifacts
Artifacts can be created and managed as entities with the console. You can access them from the dashboard or the left menu. You can:
createa new artifactexpandan artifact to see its 5 latest versionsshowthe details of an artifacteditan artifactdeletean artifactfilterartifacts by name and kind
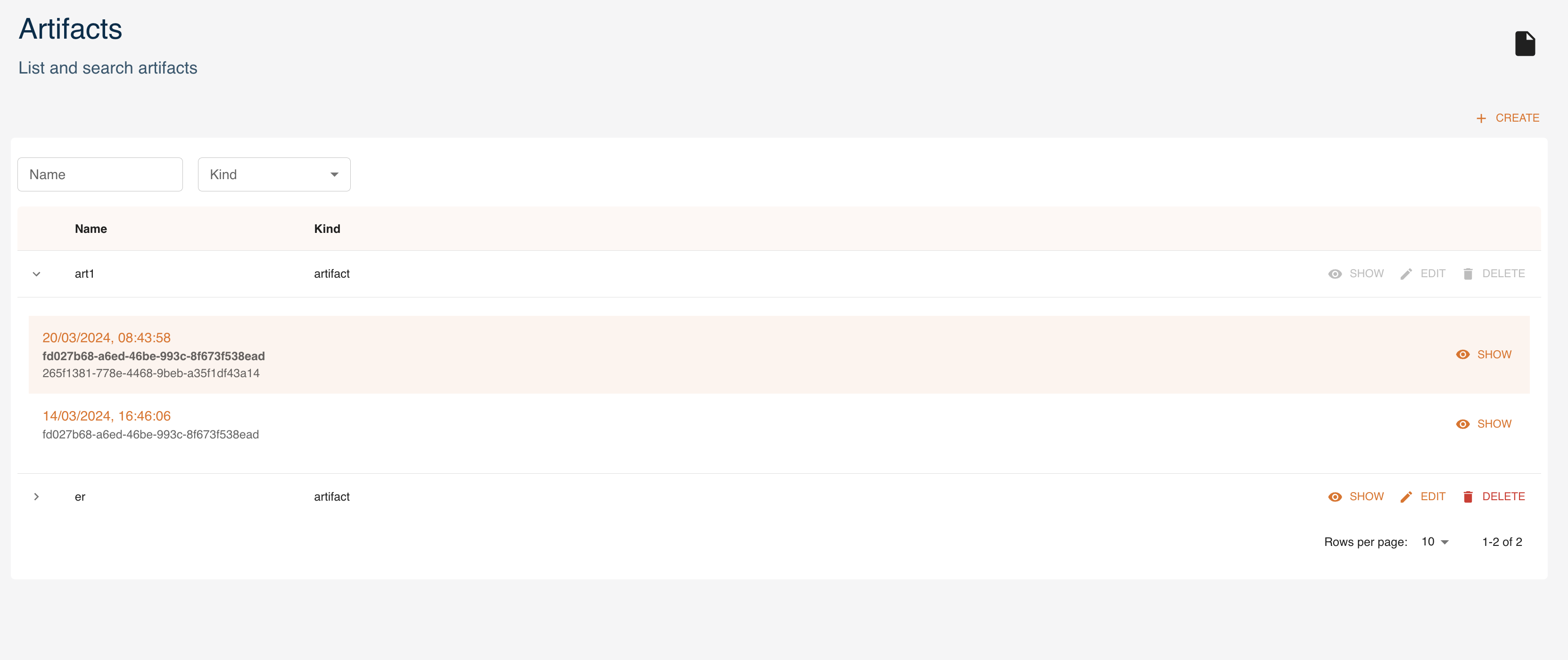
Here we analyze how to create, read, update and delete Artifacts using the UI, similarly to what is done with the SDK.
Create
Click CREATE and a form will be shown:
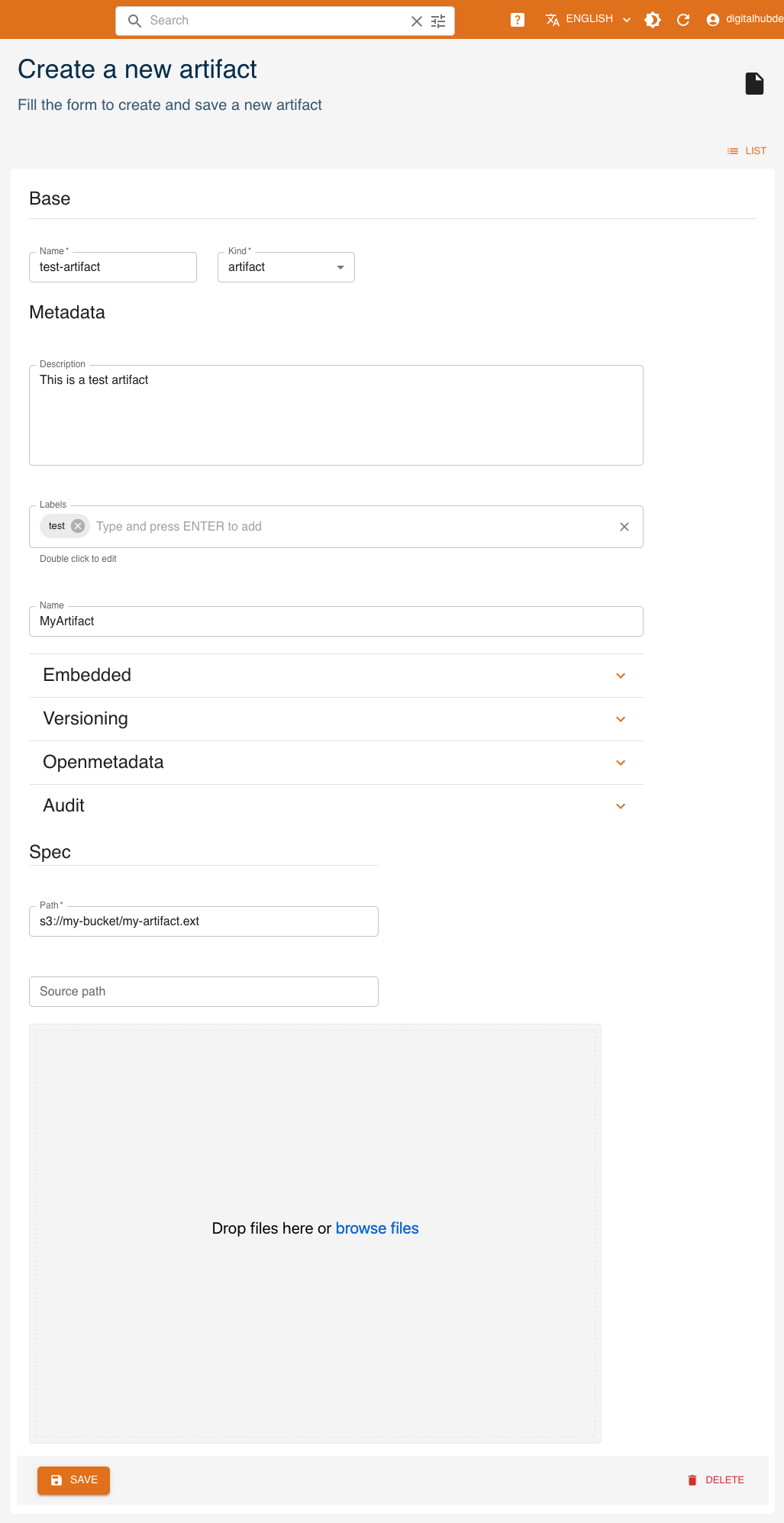
Mandatory fields are:
Name: name and identifier of the artifactKind: kind of the artifact- (Spec)
Path: remote path where the artifact is stored
Other fields are optional and may be updated later.
- (Metadata)
Name: name of the artifact - (Metadata)
Description: a human-readable description of the artifact - (Metadata)
Version: version of the artifact - (Metadata)
Labels: list of labels - (Spec)
Source path: local path to the artifact, used in case of upload into remote storage
Read
Click SHOW to view an artifact's details.
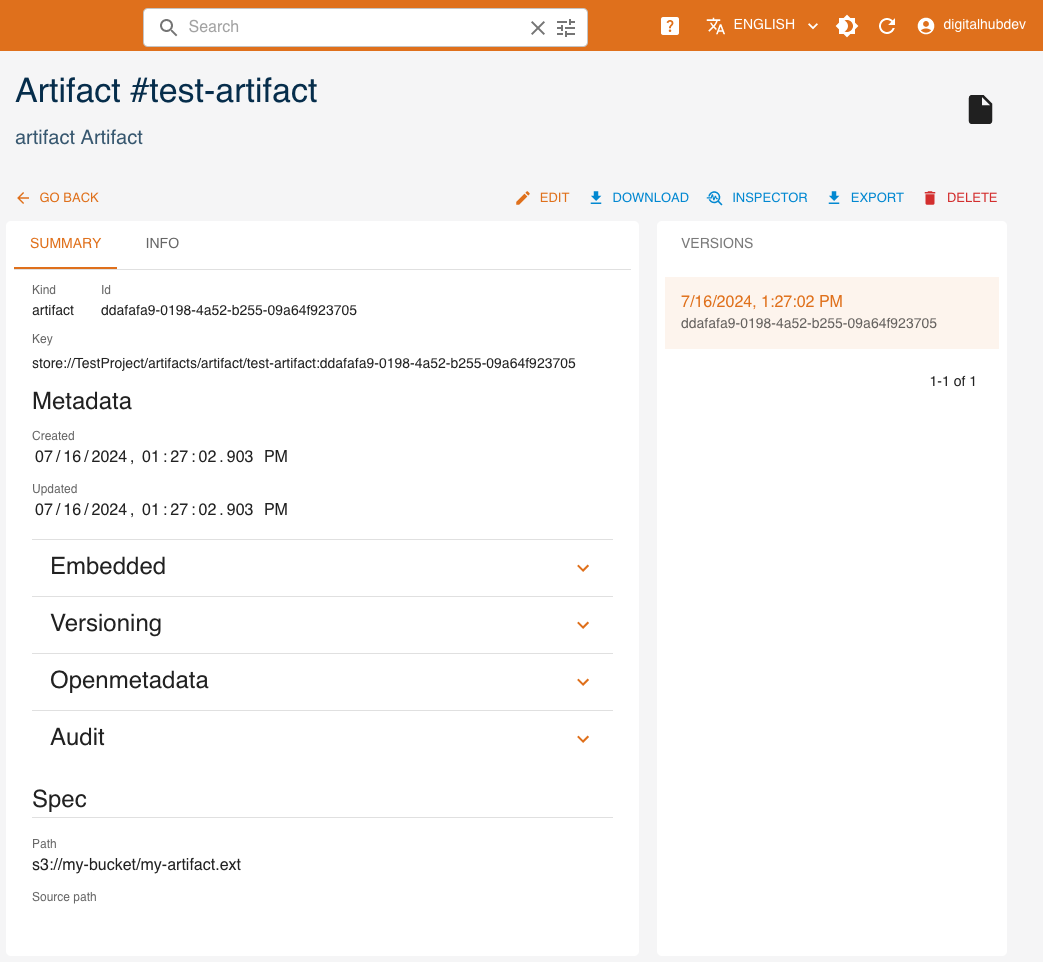
On the right side, all versions of the resource are listed, with the current one highlighted. By clicking a different version, values displayed will change accordingly.
The INSPECTOR button will show a dialog containing the resource in JSON format.
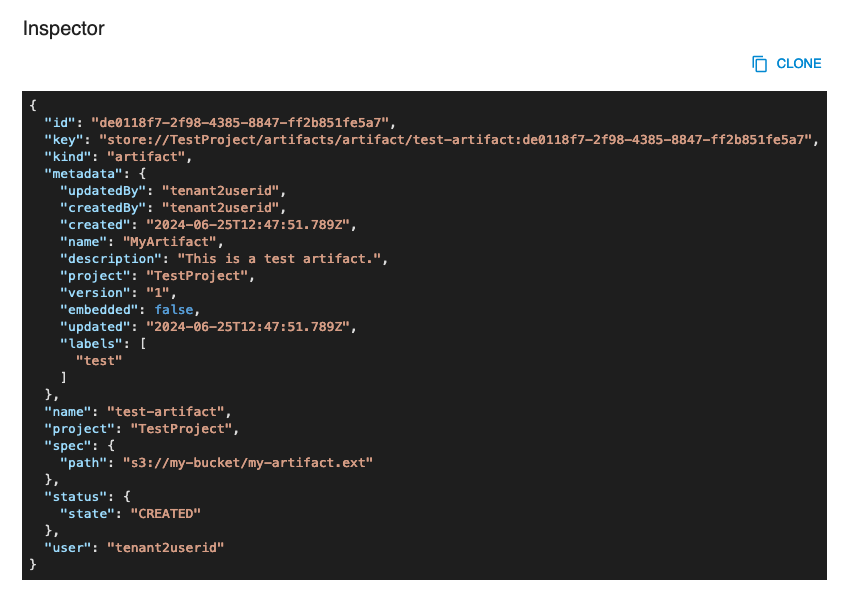
The EXPORT button will download the resource's information as a yaml file.
Update
You can update an artifact by clicking EDIT. Greyed-out fields may not be updated.
Delete
You can delete an artifact from either its detail page or the list of artifacts, by clicking DELETE.
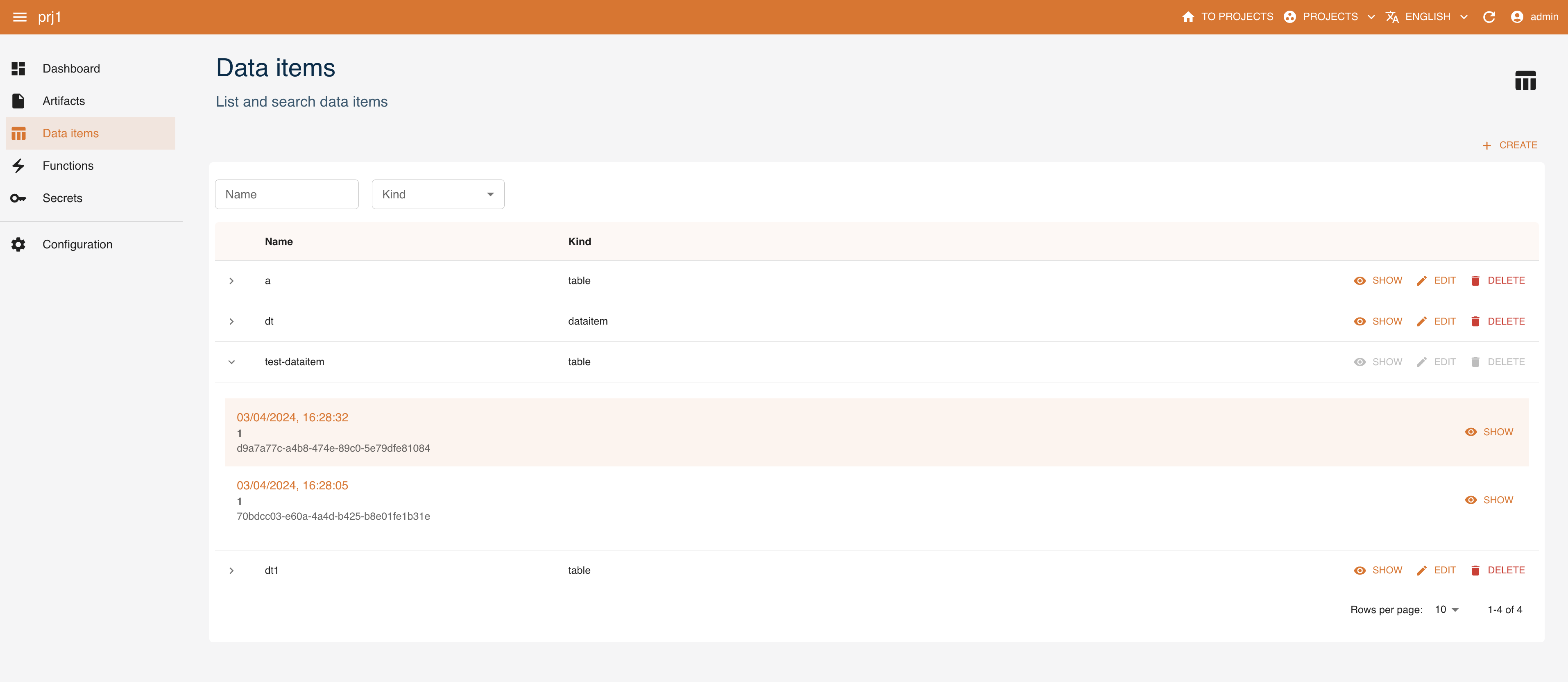
Data items
Data items can be created and managed as entities with the console. You can access them from the dashboard or the left menu. You can:
createa new data itemexpanda data item and see its 5 latest versionsshowthe details of a data itemedita data itemdeletea data itemfilterdata items by name and kind
Here we analyze how to create, read, update and delete data items using the UI, similarly to what is done with the SDK.
Create
Click CREATE and a form will be shown:
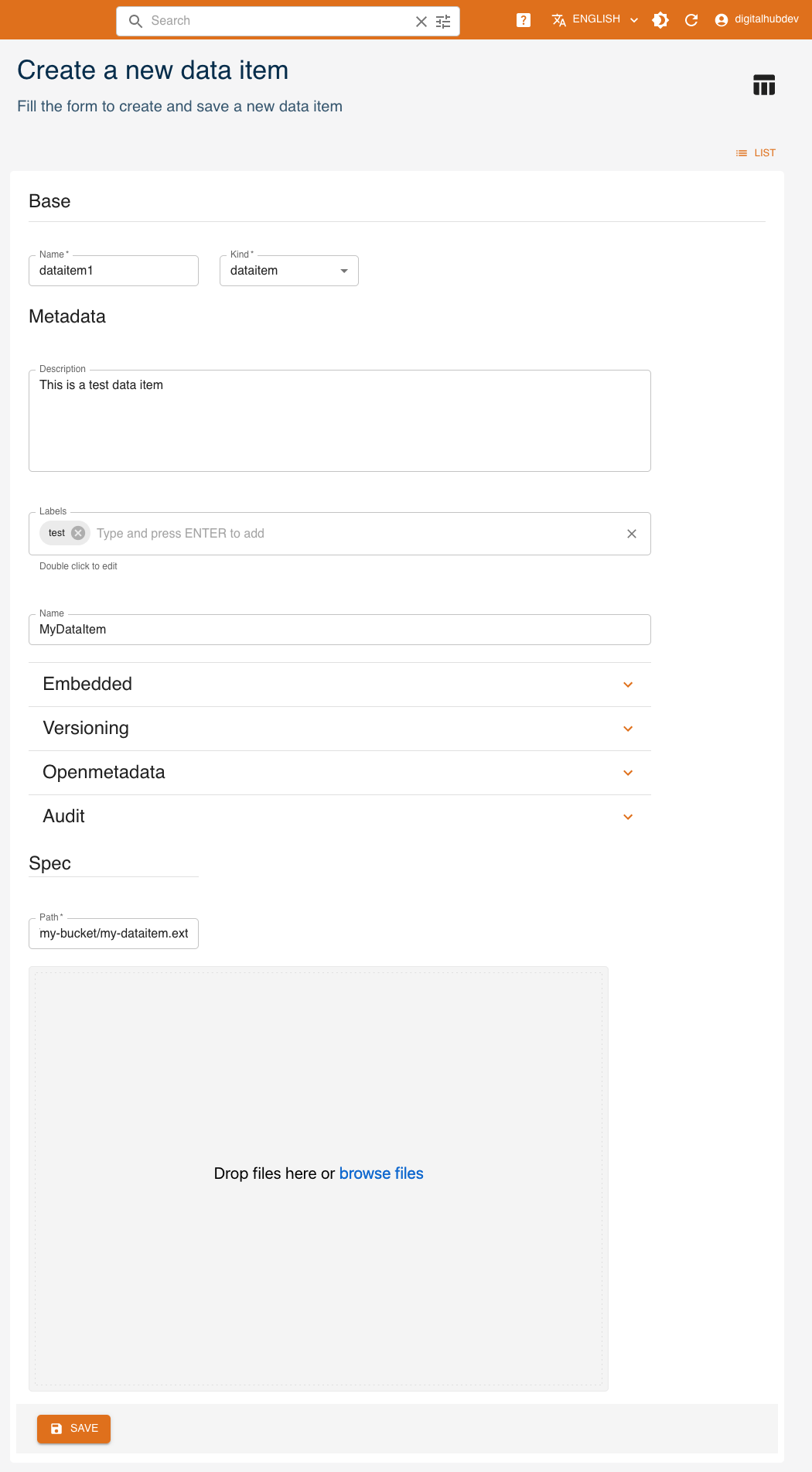
Mandatory fields are:
Name: name of the dataitemKind: kind of the dataitem- (Spec)
Path: remote path where the data item is stored
Other fields are optional and may be updated later:
- (Metadata)
Name: name of the data item - (Metadata)
Description: a human-readable description - (Metadata)
Version: version of the data item - (Metadata)
Updated: date of last modification - (Metadata)
Labels: list of labels - (Spec)
Source path: local path of the data item, used in case of upload into remote storage
Kind
There are 2 possible kinds for dataitems:
Dataitem: indicates it is a generic data item. There are no specific attributes in the creation page.table: indicates that the data item points to a table. The optional parameter is the schema of the table in table_schema format.
Read
Click SHOW to view a data item's details.
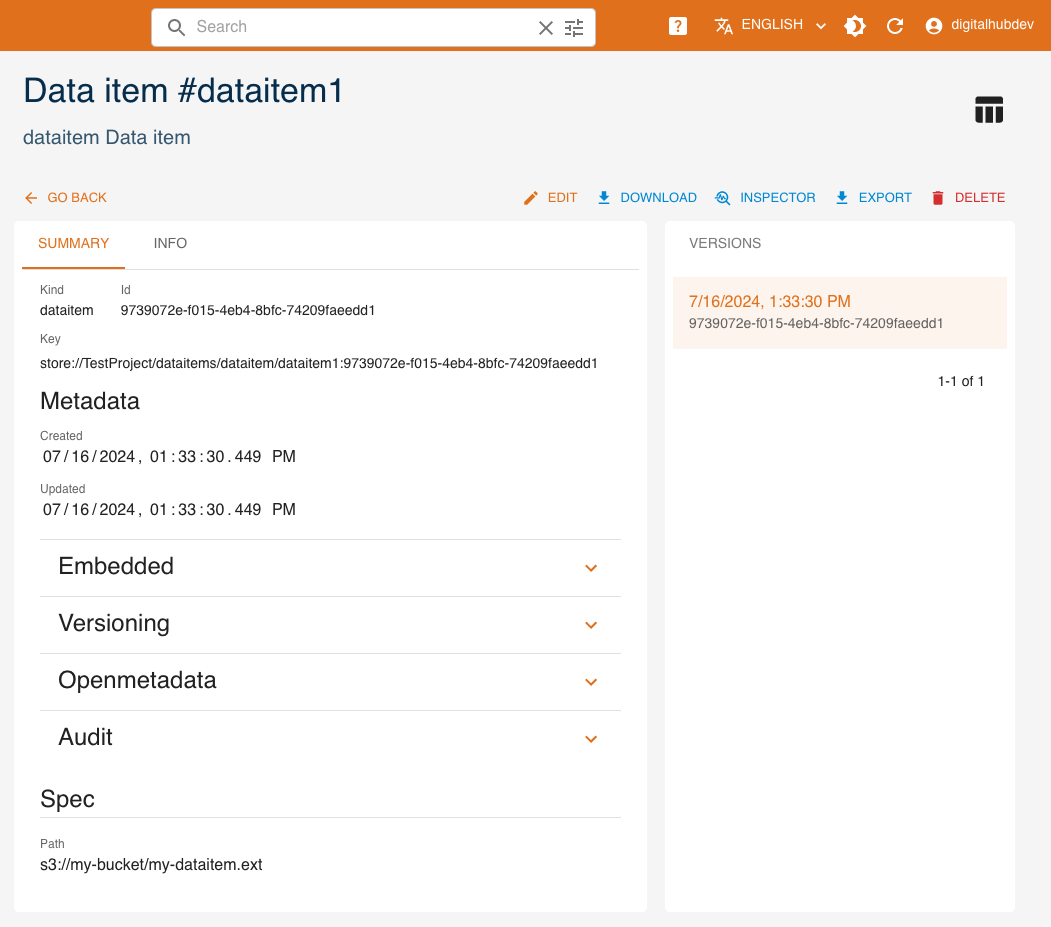
Based on the kind, there may be a schema, indicating that the dataitem point to a table.
On the right side, all versions of the resource are listed, with the current one highlighted. By clicking a different version, values displayed will change accordingly.
The INSPECTOR button will show a dialog containing the resource in JSON format.
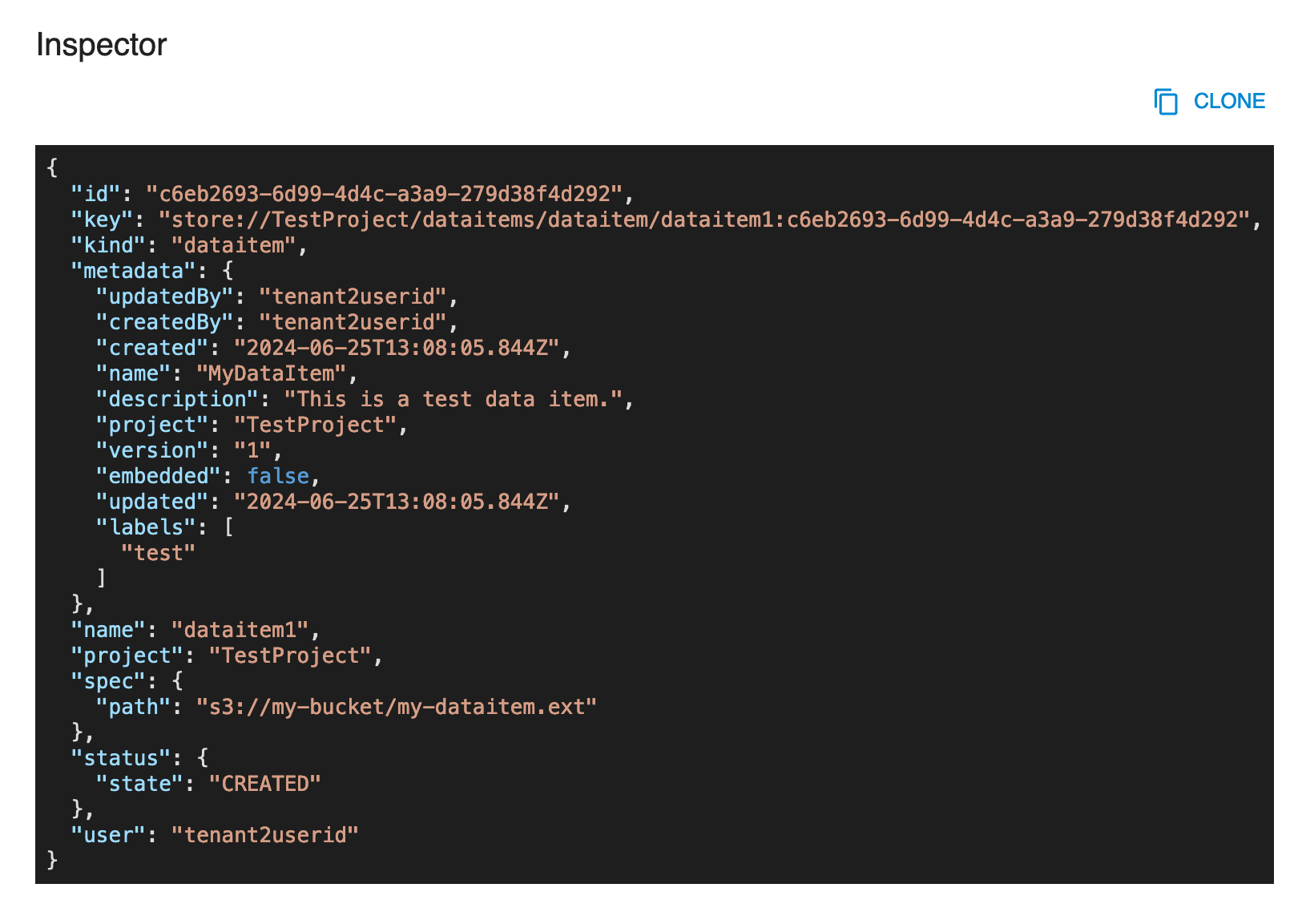
The EXPORT button will download the resource's information as a yaml file.
Update
You can update a data item by clicking EDIT. Greyed-out fields may not be updated.
Delete
You can delete a data item from either its detail page or the list of data items, by clicking DELETE.
Managing data with SDK
Artifacts
Artifacts (ARTIFACT) are (binary) objects stored in one of the artifact stores of the platform, and available to every process, module and component as files (or data streams).
Artifacts can be created and managed as entities with the SDK CRUD methods. This can be done directly from the package or through the Project object.
To manage artifacts, you need to have the digitalhub_core layer installed.
In the first section, we will see how to create, read, update and delete artifacts.
In the second section, we will see what can be done with the Artifact object.
Artifact Management via SDK
An artifact can be managed with the following methods.
new_artifact: create a new artifactget_artifact: get an artifactupdate_artifact: update an artifactdelete_artifact: delete an artifactlist_artifacts: list all artifacts
This is done in two ways. The first is through the SDK and the second is through the Artifact object.
Example:
import digitalhub as dh
project = dh.get_or_create_project("my-project")
## From library
artifact = dh.new_artifact(project="my-project",
name="my-artifact",
kind="artifact",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext")
## From project
artifact = project.new_artifact(name="my-artifact",
kind="artifact",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext")
The syntax is the same for all CRUD methods. The following sections describe how to create, read, update and delete an artifact, focusing on managing artifacts through the library. If you want to manage artifacts from the project, you can use the Project object and avoid having to specify the project parameter.
Create
To create an artifact you can use the new_artifact() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the artifact will be createdname: the name of the artifactkind: the kind of the artifactpath: the remote path where the artifact is stored
Optional parameters are:
uuid: the uuid of the artifact (this is automatically generated if not provided). Must be a valid uuid v4.description: the description of the artifactsource: the remote source of the artifact (git repository)labels: the labels of the artifactembedded: whether the artifact is embedded or not. IfTrue, the artifact is embedded (all the spec details are expressed) in the project. IfFalse, the artifact is not embedded in the projectsrc_path: local path of the artifact, used in case of upload into remote storagekwargs: keyword arguments passed to the spec constructor
Example:
artifact = dh.new_artifact(project="my-project",
name="my-artifact",
kind="artifact",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext")
Read
To read an artifact you can use the get_artifact() or import_artifact() methods. The first one searches for the artifact into the backend, the second one loads it from a local yaml.
Get
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the artifact will be created
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the artifact as identifier. It returns the latest version of the artifactentity_id: to use the uuid of the artifact as identifier. It returns the specified version of the artifactkwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
artifact = dh.get_artifact(project="my-project",
entity_name="my-artifact")
artifact = dh.get_artifact(project="my-project",
entity_id="uuid-of-my-artifact")
Import
Mandatory parameters are:
file: file path to the artifact yaml
Example:
artifact = dh.import_artifact(file="./some-path/my-artifact.yaml")
Update
To update an artifact you can use the update_artifact() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
artifact: artifact object to be updated
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
artifact = dh.new_artifact(project="my-project",
name="my-artifact",
kind="artifact",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext")
artifact.metadata.description = "My new description"
artifact = dh.update_artifact(artifact=artifact)
Delete
To delete an artifact you can use the delete_artifact() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the artifact exists
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the artifact as identifierentity_id: to use the uuid of the artifact as identifierdelete_all_versions: ifTrue, all versions of the artifact will be deleted. Mutually exclusive with theentity_idparameter.kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
artifact = dh.new_artifact(project="my-project",
name="my-artifact",
kind="artifact",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext")
dh.delete_artifact(project="my-project",
entity_id=artifact.id)
List
To list all artifacts you can use the list_artifacts() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project containing the artifacts
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
artifacts = dh.list_artifacts(project="my-project")
Artifact object
The Artifact object is built using the new_artifact() method. There are several variations of the Artifact object based on the kind of the artifact. The SDK supports the following kinds:
artifact: represents a generic artifact
For each different kind, the Artifact object has a different set of methods and different spec, status and metadata.
All the Artifact kinds have a save() and an export() method to save and export the entity artifact into backend or locally as yaml.
To create a specific artifact, you must use the desired kind in the new_artifact() method.
Artifact
The artifact kind indicates that the artifact is a generic artifact.
There are no specific spec parameters.
The artifact kind has the following methods:
as_file(): collects the artifact into a local temporary filedownload(): downloads the artifact into a specified pathupload(): uploads the artifact to a specified path
As file
The as_file() method returns the artifact as a temporary file. The file is not automatically deleted when the program ends.
The method returns the path of the downloaded artifact.
Download
The download() method downloads the artifact into a specified path.
The method returns the path of the downloaded artifact.
The method accepts the following parameters:
target: remote path of the artifact to be downloaded (eg.s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext). By default, uses thespecpath.dst: local path where the artifact will be downloaded. By default, it is in the current working directoryoverwrite: ifTrue, the target path will be overwritten if it already exists
Upload
The upload() method uploads the artifact to a specified path.
The method returns the path of the uploaded artifact.
The method accepts the following parameters:
source: local path of the artifact to be uploadedtarget: remote path of the artifact to be uploaded (eg.s3://my-bucket/my-artifact.ext). By default, uses thespecpath.
Data items
Data items (DATAITEM) are data objects which contain a dataset of a given type, stored in an addressable repository and accessible to every component able to understand the type (kind) and the source (path). Do note that data items could be stored in the artifact store as artifacts, but that is not a dependency or a requirement.
Dataitems can be created and managed as entities with the SDK CRUD methods. This can be done directly from the package or through the Project object.
To manage dataitems, you need to have the digitalhub_data layer installed.
In the first section, we will see how to create, read, update and delete dataitems.
In the second section, we will see what can be done with the Dataitem object.
Data item management via SDK
A data item can be managed with the following methods.
new_dataitem: create a new data itemget_dataitem: get a data itemupdate_dataitem: update a data itemdelete_dataitem: delete a data itemlist_dataitems: list all data items
This is done in two ways. The first is through the SDK and the second is through the Dataitem object.
Example:
import digitalhub as dh
project = dh.get_or_create_project("my-project")
## From library
dataitem = dh.new_dataitem(project="my-project",
name="my-dataitem",
kind="dataitem",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-dataitem.ext")
## From project
dataitem = project.new_dataitem(name="my-dataitem",
kind="dataitem",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-dataitem.ext")
The syntax is the same for all CRUD methods. The following sections describe how to create, read, update and delete a data item, focusing on managing data items through the library. If you want to manage data items from the project, you can use the Project object and avoid having to specify the project parameter.
Create
To create a data item you can use the new_dataitem() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: project in which the data item will be createdname: name of the data itemkind: kind of the data itempath: remote path where the data item is stored
Optional parameters are:
uuid: uuid of the data item (this is automatically generated if not provided). Must be a valid uuid v4.description: description of the data itemsource: remote source of the data item (git repository)labels: list of labelsembedded: whether the data item is embedded or not. IfTrue, the data item is embedded (all the spec details are expressed) in the project. IfFalse, the data item is not embedded in the project.kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the spec constructor
Example:
dataitem = dh.new_dataitem(project="my-project",
name="my-dataitem",
kind="dataitem",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-dataitem.ext")
Read
To read a data item you can use the get_dataitem() or import_dataitem() methods. The first one searches for the data item into the backend, the second one load it from a local yaml.
Get
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the data item will be created
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the data item as identifier. It returns the latest version of the data item.entity_id: to use the uuid of the data item as identifier. It returns the specified version of the data item.kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
dataitem = dh.get_dataitem(project="my-project",
entity_name="my-dataitem")
dataitem = dh.get_dataitem(project="my-project",
entity_id="uuid-of-my-dataitem")
Import
Mandatory parameters are:
file: file path to the dataitem yaml
Example:
dataitem = dh.import_dataitem(file="./some-path/my-dataitem.yaml")
Update
To update a data item you can use the update_dataitem() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
dataitem: data item object to be updated
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
dataitem = dh.new_dataitem(project="my-project",
name="my-dataitem",
kind="dataitem",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-dataitem.ext")
dataitem.metadata.description = "My new description"
dataitem = dh.update_dataitem(dataitem=dataitem)
Delete
To delete a data item you can use the delete_dataitem() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project in which the data item exists
Optional parameters are:
entity_name: to use the name of the data item as identifierentity_id: to use the uuid of the data item as identifierdelete_all_versions: ifTrue, all versions of the data item will be deleted. Its mutually exclusive with theentity_idparameterkwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
dataitem = dh.new_dataitem(project="my-project",
name="my-dataitem",
kind="dataitem",
path="s3://my-bucket/my-dataitem.ext")
dh.delete_dataitem(project="my-project",
entity_id=dataitem.id)
List
To list all data items you can use the list_dataitems() method.
Mandatory parameters are:
project: the project containing the data items
Optional parameters are:
kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the client that communicates with the backend
Example:
dataitems = dh.list_dataitems(project="my-project")
Dataitem object
The Dataitem object is built using the new_dataitem() method. There are several variations of the Dataitem object based on the kind of the data item. The SDK supports the following kinds:
dataitem: represents a generic data itemtable: represents a table data item
For each different kind, the Dataitem object has a different set of methods and different spec, status and metadata.
To create a specific data item, you must use the desired kind in the new_dataitem() method.
All the Dataitem kinds have a save() and an export() method to save and export the entity data item into backend or locally as yaml.
Dataitem
The dataitem kind indicates that the data item is a generic data item.
There are no specific spec parameters nor specific method exposed. It acts as a generic data item.
Table
The table kind indicates that the data item point to a table.
The optional spec parameters are:
schema: the schema of the table in table_schema format
The table kind also has the following methods:
as_df(): to collect the data in a pandas dataframewrite_df(): to write the data item as parquet
Read table
The as_df() method returns the data in a pandas dataframe.
The method accepts the following parameters:
format: the format of the data. If not provided, the format will be inferred from the file extension. We support ONLY parquet or csv.kwargs: keyword arguments passed to the pandasread_parquetorread_csvmethod
Write table
The write_df() method writes the data item as parquet.
The method accepts the following parameters:
target_path: the path of the target parquet file. If not provided, the target path will created by the SDK and the data item will be stored in the default storekwargs: keyword arguments passed to the pandasto_parquetmethod