User attributes
As previously introduced, user identities are composed by binding an account to one or more sets of attributes, which are properties describing an aspect of the user. Attributes are stored in sets as key-value pairs, with the option of adhering to a schema.
By default, every user identity will possess at least a single attribute set, reporting all the properties exposed by the provider from the account itself. For example, the internal provider exports the username and email, along with details about the account registration, expiration etc. All these properties are mapped to an identity provider specific set, with both the content and the schema fully managed by the idp.
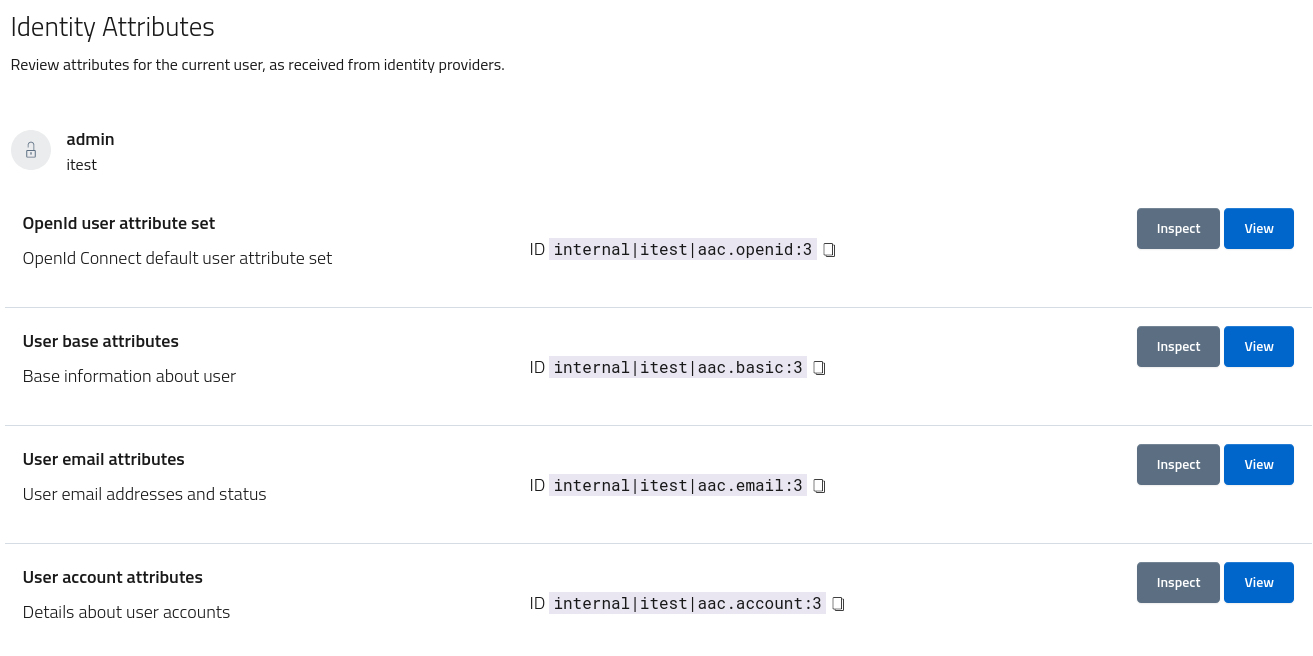
Core attribute sets
In order to consume this attribute set in a standardized and uniform way, AAC defines a number of attribute sets with a specific schema and usage:
- base attributes are core information such as name,surname,email,username
- email attributes are core information on email address and email verification
- account attributes are core information about the account, such as userid, provider, authority, realm
- openid attributes are optional information described according to the OpenID Connect profile, such as first and last name, email address, preferred username, language etc.
These attribute sets are derived from the single idp attribute set by AAC, via mapping and translation. This process is automatic, and can be tuned and tailored to specific scenarios by editing idp attributes at login, via custom mapping (see the expert documentation).
Additional attribute sets
In addition to core sets, which are defined by AAC and whose definitions are immutable, administrators can define schemas which describe properties as sets: by defining the name, key, type of attributes and registering the definition as attribute set, administrators will be able to define their custom properties in accordance to their scenario.
Attribute sets
Attribute sets are managed from the realm console via a dedicated section, accessible by navigating to attributes > attribute sets
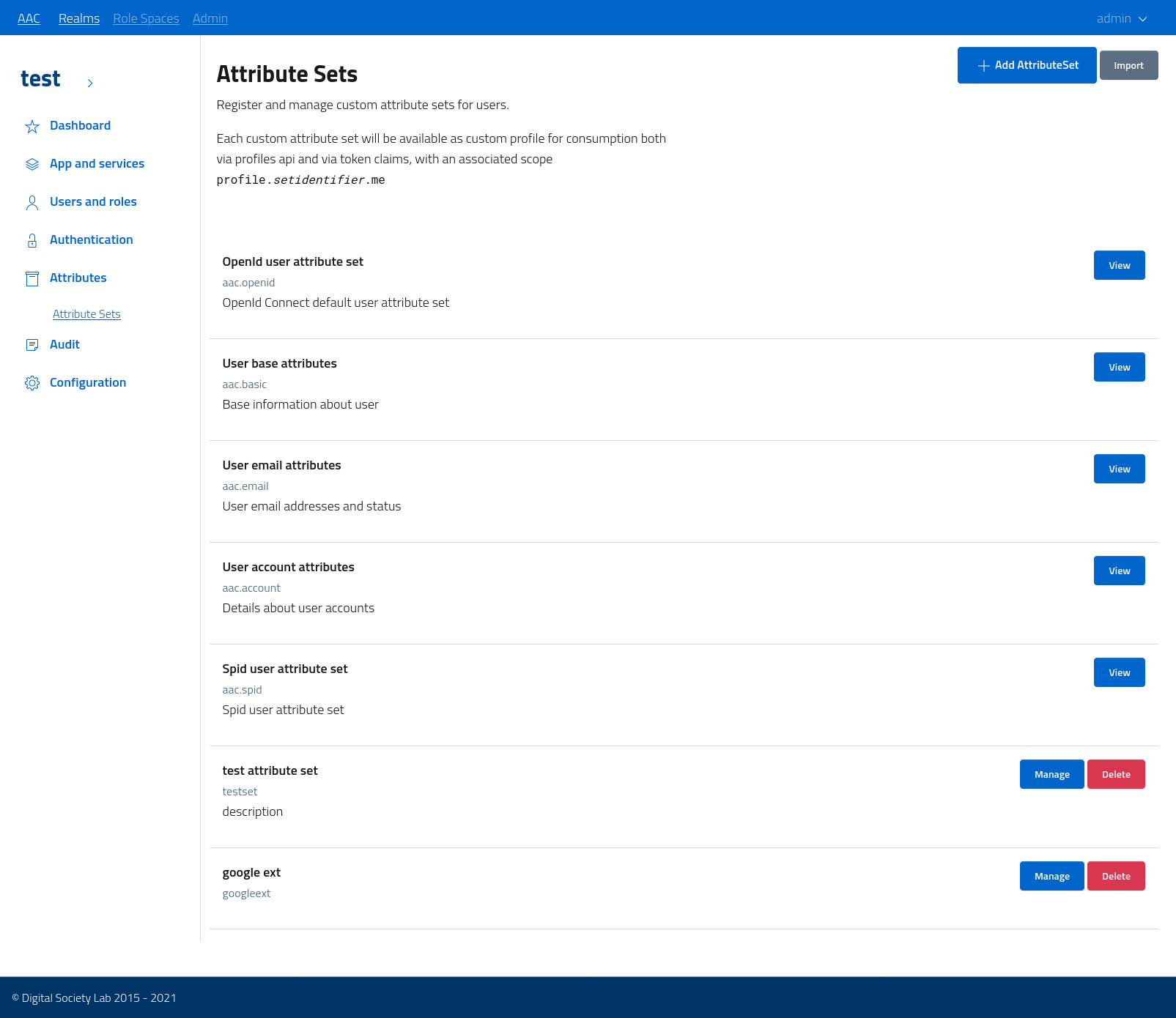
The section will report both the core and the custom attribute sets, with the first exposed as read-only for review and the second as read-write.
To create a new set click the add button and fill in the dialog with the following properties:
- id a globally unique identifier for the set
- name a descriptive label
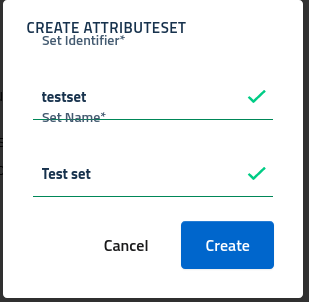
By adding a new set the system will register the model and prepare an empty attribute set, ready for customization. Open the manage section by clicking on the action button.
Attribute set management
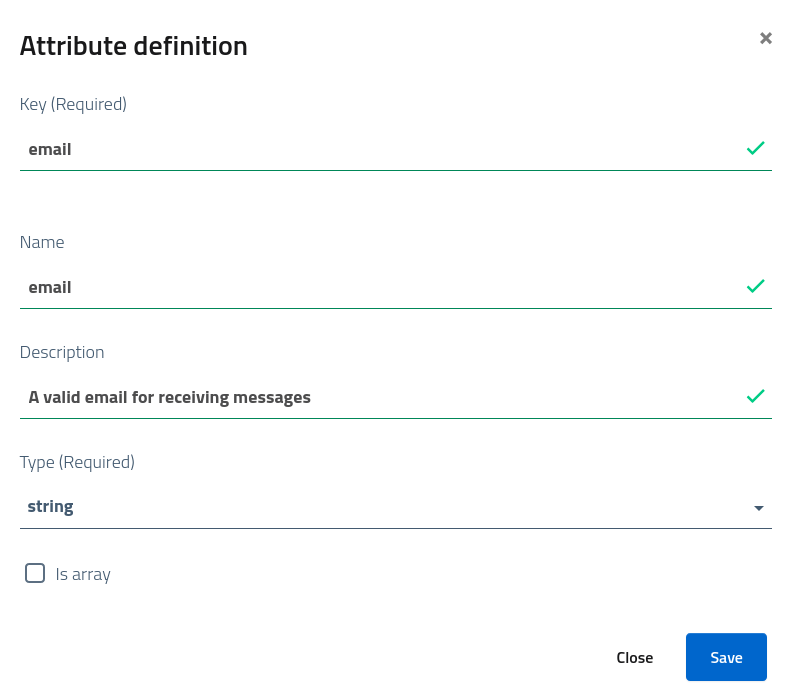
The section is dedicated to the definition of an attribute set in terms of model and attributes.
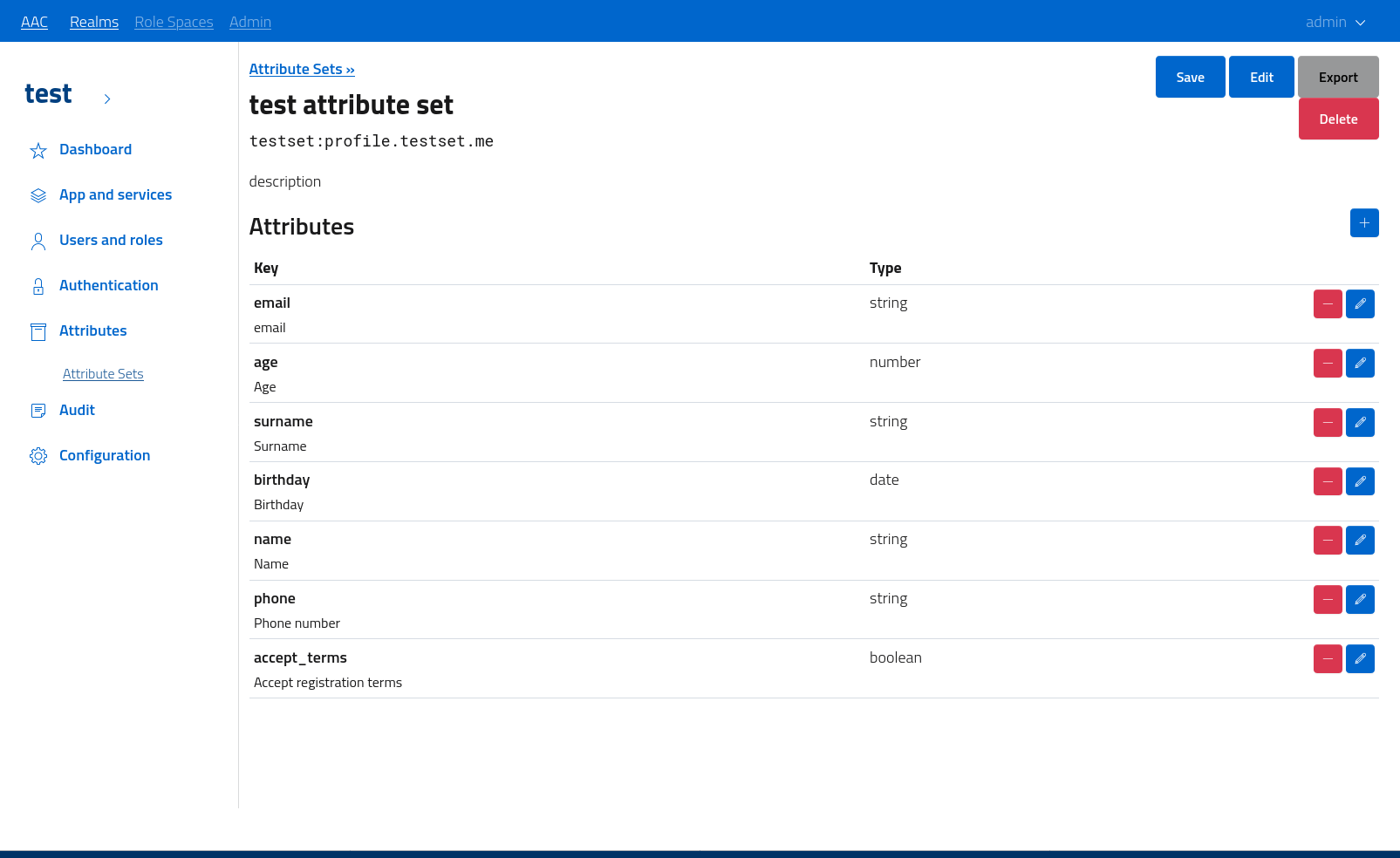
The management console will let administrators define the list of attributes. Each attribute needs to register the key, a descriptive name and the field type. It is fundamental to select an appropriate field among those available to ensure proper attribute parsing, handling and translation.
Attribute sets usage
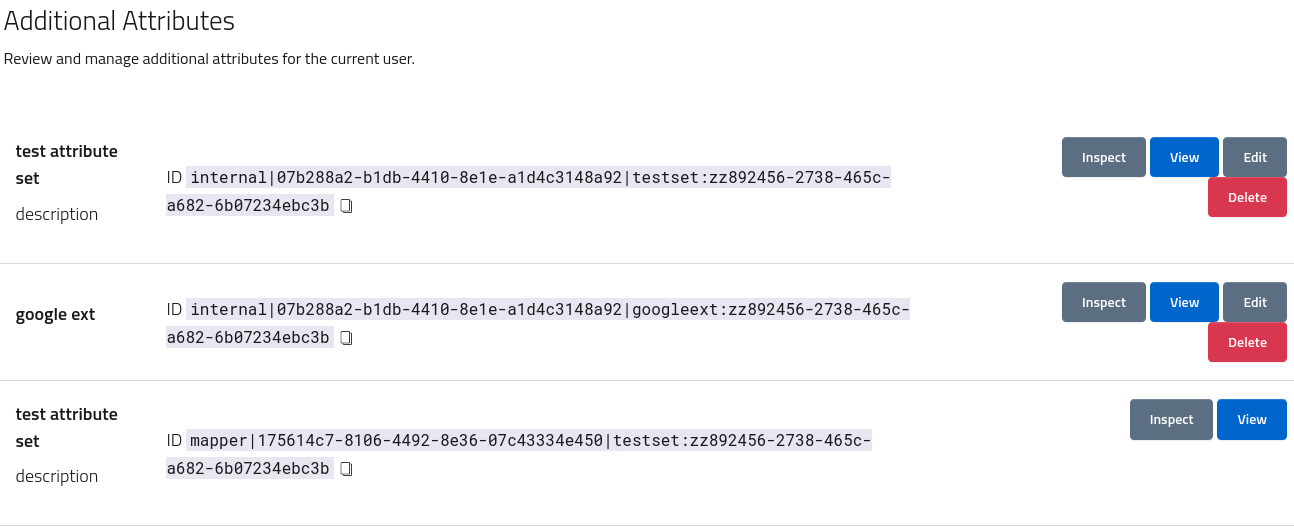
When custom attribute sets are defined, user models will contain the instantiation of such models, according to the definition, as operated by attribute providers. To review and edit attributes open the user console at users and roles > users, select a subject and the navigate to the attributes section.
The interface will list every populated custom attribute set after the core models, and where supported by providers offer administrators the ability to either edit or create as new. All the custom attribute sets can also be deleted, but be aware that at the following login attribute providers can recreate and persist them again, according to the most up-to-date information and their generation rules.
Attribute providers
AAC offers administrators the ability to integrate attributes gathered from the identity providers via the registration of attribute providers: additional services which receive in input a given user principal and return one or more additional attribute sets, according to a selected schema.
The idea is to offer an extension point during the authentication process, which can be used to integrate external information or manipulate the received properties in a custom way.
Many different provider authorities are available out of the box, such as:
- mappers, which will receive a list of properties and map them to new attributes according to the schema
- code, which will execute a function to translate existing properties into new one
- webhook, which will call an external API to receive back one or more attribute sets.
- internal, which will provide an internal key-value store where users or administrators will manually register new properties
Attribute providers console
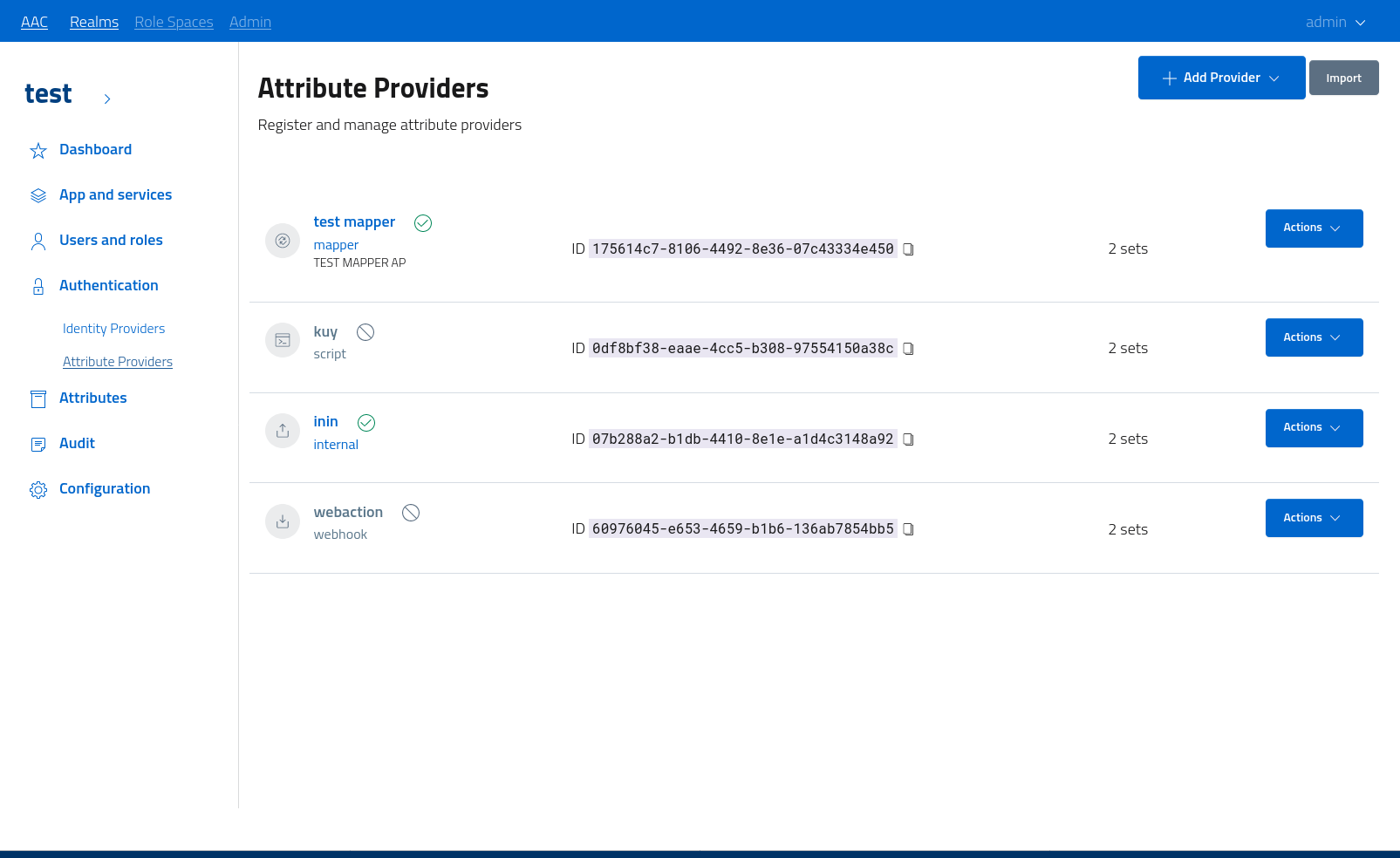
To register and manage providers access the console by navigating to authentication > attribute providers. By default, the list will be empty: only core attribute sets are populated, by identity providers.
Add a new provider via toolbar action: select an authority and fill in a descriptive name.
Every attribute provider can be active or inactive: administrators can change the state by enabling and disabling providers at need.
Do note that every active attribute provider will be invoked in parallel during the authentication process: there is no relation between different providers and every one will receive in input the same user model, as gathered from the identity provider. Only after all the invocations are concluded AAC will merge the results, and associated all the custom attribute sets to the user.
Also note that attribute sets can be duplicated: every single instantiation will be defined by binding the set together with the source user and the processing provider. As such, a single provider can return a single instance of any associated attribute set, but different providers can also return an instance for the same set, with different values: it is up to consumers to choose which information they are interested in. As general rule, it is advisable to define a specific attribute set for every provider to avoid overlapping, and then perform any map or merge at consumption time via profiles.
Attribute provider management
The management console exposes a configuration section common to all providers, with basic settings such as name,description, and then an advanced section specific for the given authority.
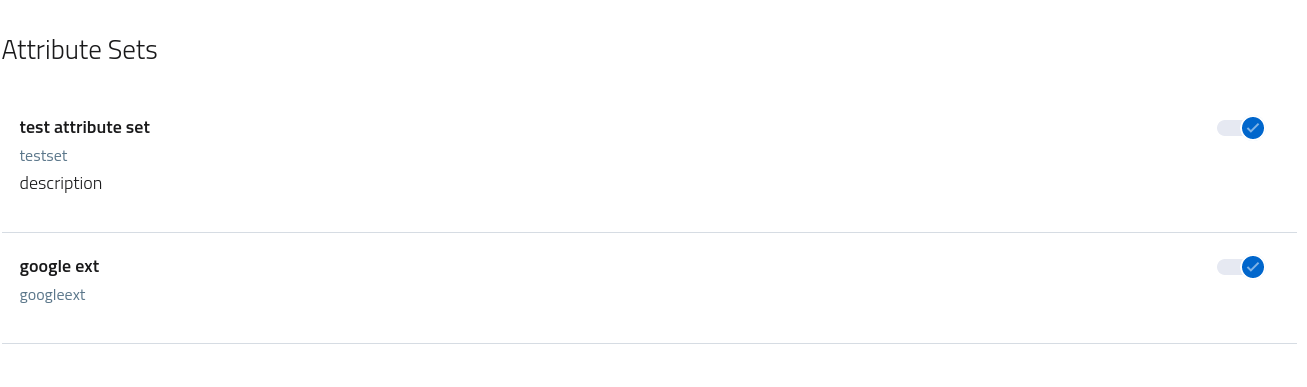
In order to let the provider offer valid results, ready to be merged into the user model, administrators will need to link all the custom attribute sets which can be produced by the given provider. AAC will parse the result and then evaluate the correspondence to the various schemas: only valid and registered sets will be accepted.
To link a specific set flip the correspondent toggle switch under the attribute sets section of the console.
Do note that active providers can not be updated: to persist any change it is mandatory to temporarily disable the provider, save the updates and then enable again. This flow is required to make sure that any operation currently happening is concluded before changing the registration. The toolbar offers the various action buttons to support this flow.

Attribute provider test
AAC supports the execution of a test flow for attribute providers, where the currently logged-in user is used as principal: the attribute provider will be called with the user properties simulating an authentication operation and the result will be mapped to attribute sets according to definition.
To perform the test open the attribute provider console, navigate to test and select the action. The input model and the results will be shown in the interface, along with any error message generated by the provider.

Future versions will offer the ability to mock the user principal to simulate specific scenarios.